
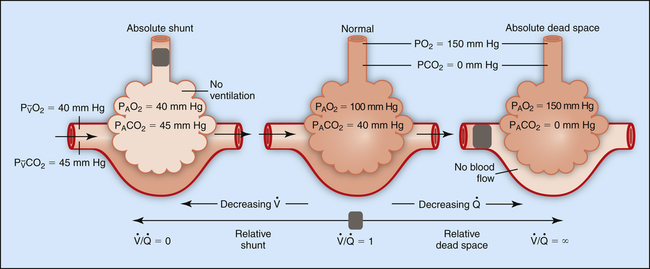
This modification is in general use today, but it comes with limitations. In 1938, Enghoff proposed replacement of PACO 2 by partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO 2), also known as the Enghoff modification. However, difficulties with measurement of PACO 2 led to rejection of this method. V D calculated using Bohr’s equation accurately measures V D,phys. Where V D is dead-space volume (i.e., volume not participating in gas exchange), V T is total exhaled volume, PACO 2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveolar air, and PeCO 2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in mixed expired air. Our results demonstrate the challenges clinicians face in interpreting an apparently simple measurement such as V D/V T. Volumetric capnography is a promising technique to calculate true Bohr dead space. Conclusionsĭifferent techniques to measure PACO 2 and PeCO 2 result in clinically relevant mean and individual differences in calculated V D/V T, particularly in patients with ARDS. For example, in patients with ARDS, V D/V Tcalculated with Enghoff-InCal was much higher than Bohr-VCap (V D/V T Enghoff-InCal = 66 ± 10 % vs.

These differences strongly affected calculated V D/V T. VCap (post-cardiac surgery bias = 0.04 ± 0.19 kPa ARDS bias = 0.03 ± 0.27 kPa) and relatively low agreement with DBag vs. There was good agreement in PeCO 2 calculated with DBag vs. PaCO 2 was higher than PACO 2, particularly in patients with ARDS (post-cardiac surgery PACO 2 = 4.3 ± 0.6 kPa vs. Subsequently, V D/V T was calculated using four methods: Enghoff-DBag, Enghoff-InCal, Enghoff-VCap, and Bohr-VCap. PeCO 2 was measured in expired air using three techniques: Douglas bag (DBag), indirect calorimetry (InCal), and VCap. PACO 2 was measured using VCap to calculate Bohr dead space or substituted with partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO 2) to calculate the Enghoff modification. In a prospective, observational study, 15 post-cardiac surgery patients and 15 patients with ARDS were included. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate how VCap and other available techniques to measure PACO 2 and partial pressure of carbon dioxide in mixed expired air (PeCO 2) affect calculated V D/V T. Recently, a novel technique to calculate partial pressure of carbon dioxide in alveolar air (PACO 2) using volumetric capnography (VCap) was validated. However, V D/V T is rarely calculated in clinical practice, because its measurement is perceived as challenging. In patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), V D/V T has prognostic value and can be used to guide ventilator settings. Physiological dead space (V D/V T) represents the fraction of ventilation not participating in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
